How to Reduce Ransomware and Disaster Recovery Times with Data Resiliency Best Practices
When it comes to ransomware, the statistics paint a clear picture: it’s not a matter of ‘if’, it’s a matter of when. Catastrophic ransomeware strikes are becoming more frequent and more complex. Still, most organizations will admit that they’re not where they should be with regards to cybersecurity hygiene and backup usage. For many, the question itself has become overwhelming: just where do you start developing ransomware resilience?
First, let’s identify what we’re seeing from the industry going into 2025.
Attack Trends We’re Seeing
AI-Enhanced Ransomware
AI is getting smarter in a number of areas. In 2025, we expect to see AI being a driving force behind more efficient, automated ransomware attacks. Cybercriminals are going to use AI to identify vulnerabilities, evade detection, and target your high-value systems. In addition, phishing attacks will be more personalized and difficult to detect, thanks to machine learning algorithms that allow for more precise attacks.
Ransomware Targeting Vendor Infrastructure
Ransomware groups have adapted to the great migration to the cloud among many businesses. The cloud can be a vulnerable target due to the large quantity of businesses now relying on it, and in 2025 we anticipate more ransomware attacks aimed directly at cloud services, affecting multiple ecosystems. This means to achieve ransomware resilience, it’s necessary for your organization to leverage reliable and segregated backups.
Double, Triple, and Quadruple Extortion
In the past, threat actors would hit their targets for one payout before moving on. Things have changed, and it’s no longer simply about encrypting data. Attackers are ramping up their extortion techniques, demanding payment two, three, or even four times. This could involve holding customers and other third-party vendors hostage by threatening them with data exposure.
Targeting Critical Supply Chains
It happened to SolarWinds in 2020, Kaseya in 2021, and Okta in 2023. Supply chains remain tempting targets for ransomware groups. When a single vendor is compromised, the attackers are able to infiltrate an entire network of businesses. Criminals can deploy ransomware to multiple organizations at once, which means businesses need to thoroughly vet their suppliers and harden their defenses against third-party vulnerabilities.
Focus on Data Integrity Attacks
Beyond just encrypting or stealing data, attackers are beginning to target data integrity itself. Instead of simply holding your data hostage, they may corrupt or manipulate it, rendering backups useless and causing operational havoc. This emerging trend could lead to major financial and reputational damage, as it undermines trust in the accuracy and reliability of your business’s data. To combat this, businesses will need to invest in advanced monitoring systems capable of detecting even subtle changes in data integrity.
75% Suffered Ransomware Attacks in 2023
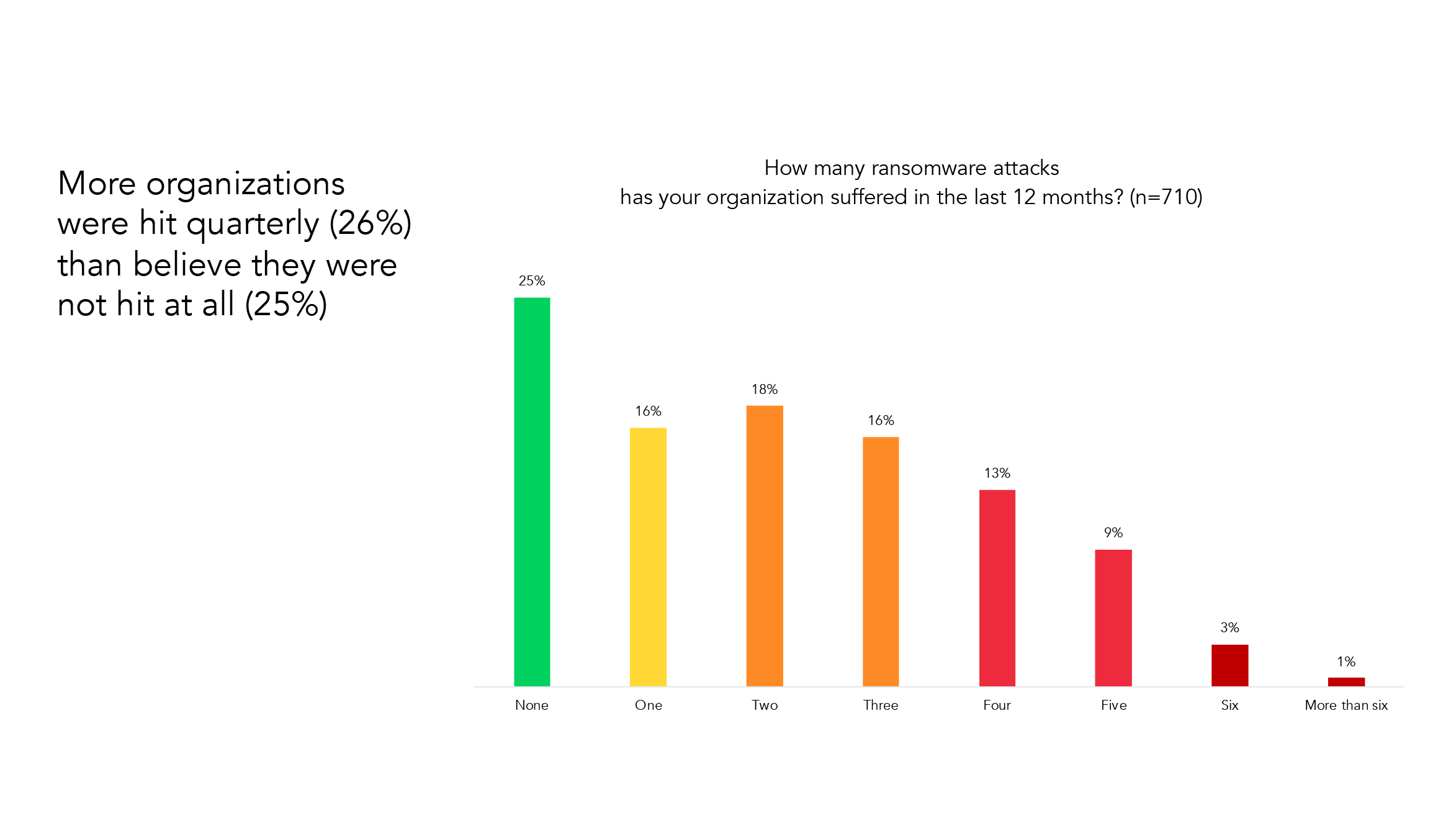
What the data has been telling us, is that three out of every four organization experience a ransomware strike. This highlights the importance for two strategies within your organization for ransomware resilience: a strategy to defend against ransomware, and a strategy for recovering from ransomware.
Furthermore, it illustrates why resiliency is so important: bad actors only need to win one time in order to successfully bring disaster to your business. Your organization needs to win consistently in order to stay protected, which means vigilance against potential threats around the clock.
As an example of this, an Atomic Data account who had not developed ransomware resilience was impacted by a major event. An employee was conducting research, and downloaded a file pertinent to their industry. The file contained a payload allowed a bad actor into the network, where they destroyed their backups, formatted tapes, and encrypted every bit of data that they could find. One mistake led to significant damages to critical business functions.
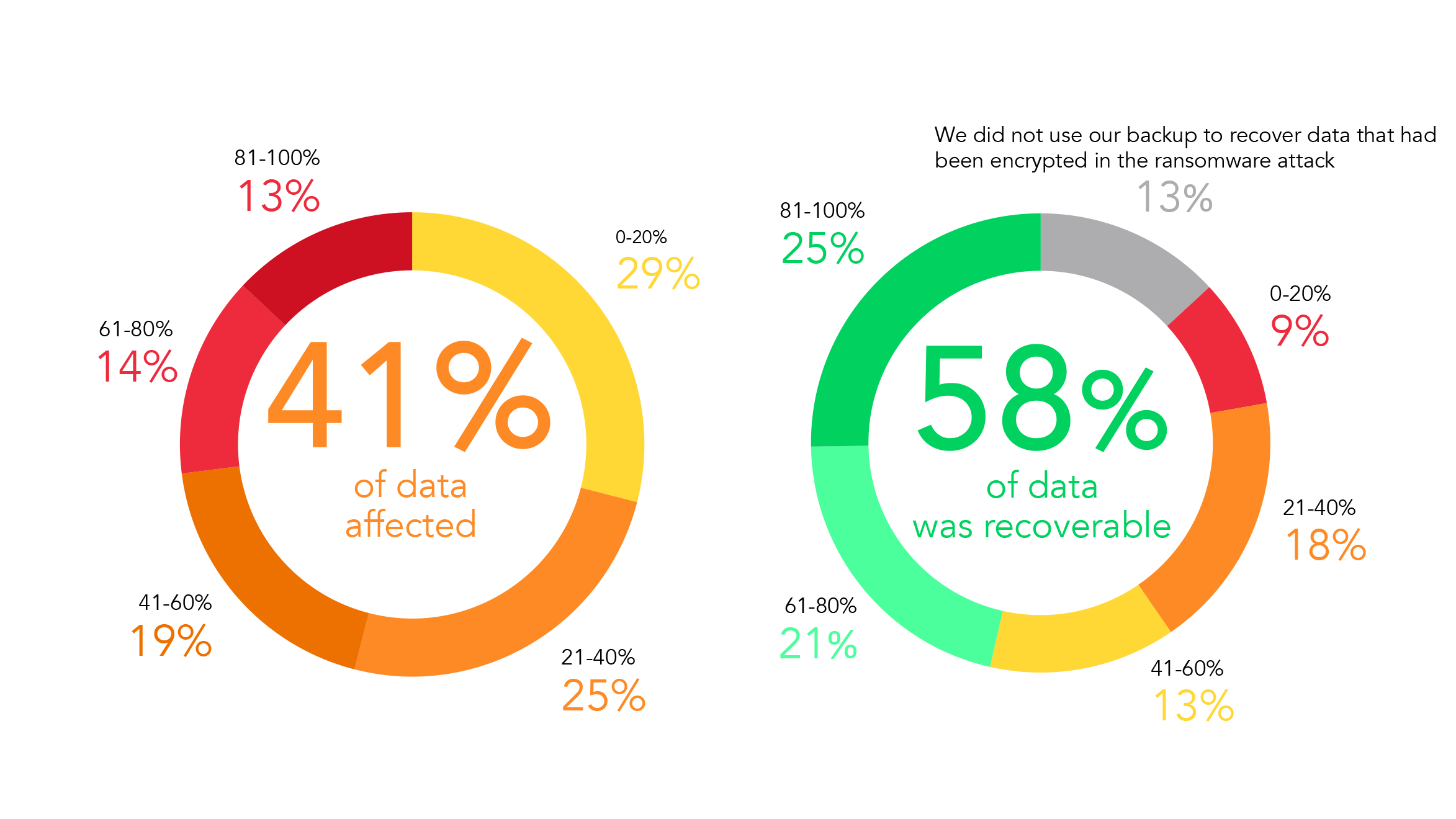
The research also shows worrying trends among the businesses targeted by ransomware. Nearly half of a target’s data is usually affected during ransomware strikes: most businesses cannot afford for half of their data to be encrypted. What this data is showing us is the importance of having multiple layers of security. Furthermore, your organization should keep tight control over data access – a laissez faire approach to permissions means that what happens to one team within your business, can impact another. Defense and mitigation is the most painless approach to avoiding data loss: many businesses that are able to retrieve their data do so by paying exorbitant ransoms – not a picture of ransomware resilience.
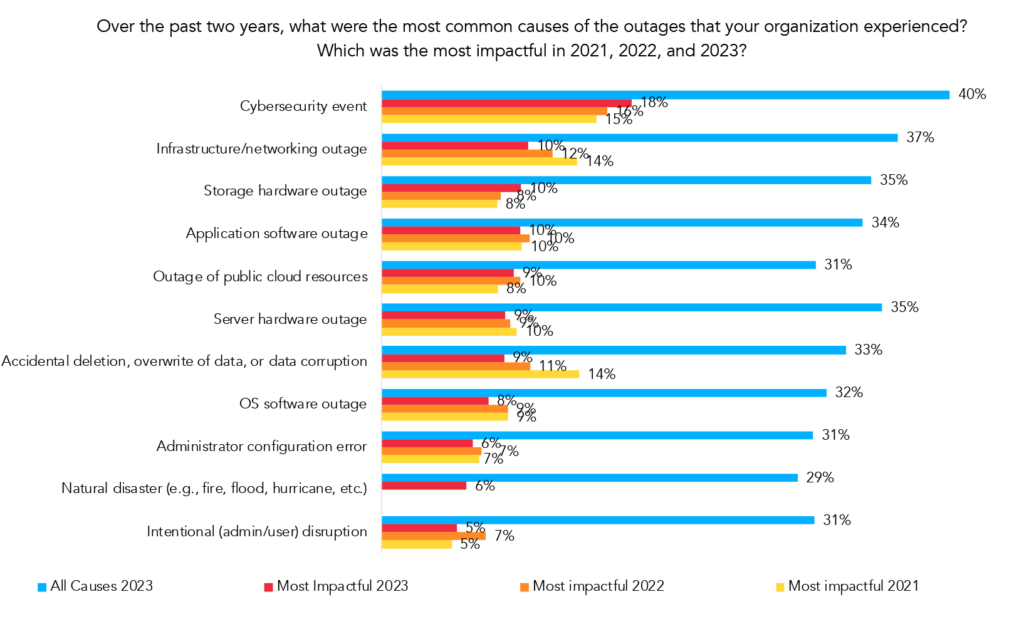
Most Common & Most Impactful Outage Events
Backups Were Targeted in 96% of Attacks
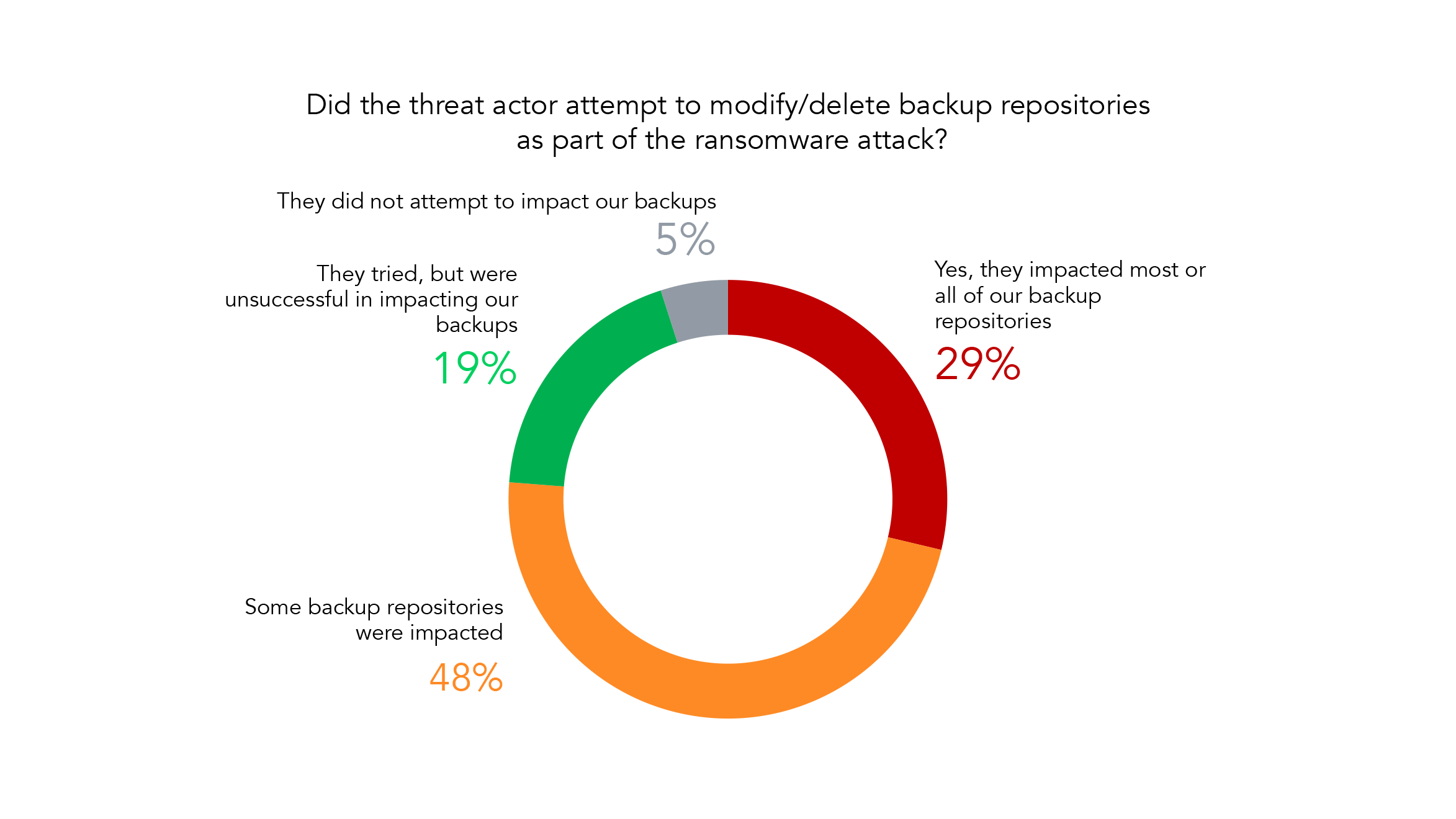
As the value of your backups grow, so does the number of attacks aimed at them. It’s more important than ever to have resilient backups – recovering from a backup is the most reliable way to get back on your feet quickly. Having backups that are offline, air gapped, or immutable is important.
Having encrypted data is also vital. Breaking modern encryption is an immense challenge for threat actors, so even in the event that your data is stolen, that encryption can prevent it from damaging you once it’s out of your hands.
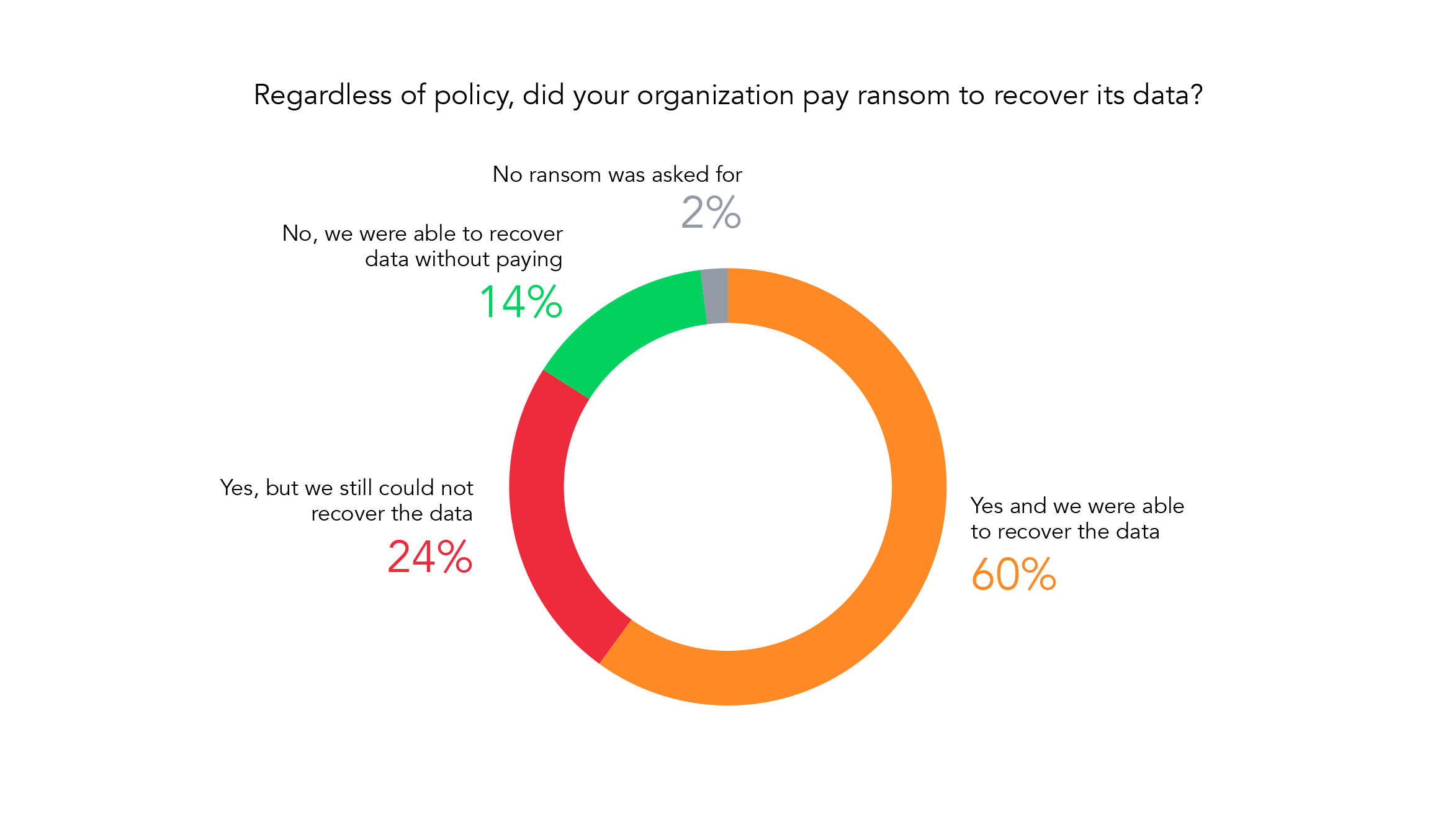
Less than 15% of organizations are able to emerge from a ransomware attack without paying. Furthermore, while it’s true that the data tells us most organizations are able to recover their data by paying a ransom, it’s important to remember that the price of the ransom is not the only cost associated with these kinds of attacks. Not only might you pay a ransom, but you’ll also need to handle the costs associated with interruptions to your operations, damage to brand image, and an increased pressure on your IT department.
Attack Prevention
As the saying goes, “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure.” A multi-angled approach to cyber-hygiene is crucial, where business-wide adoption of industry best practices pay dividends when considering the potential cost of remediating a disaster. Backups are important, and a big part of this, but the best backup is the one that you don’t need in the first place.
Atomic Data’s experts frequently speak about the three main types of risk to your business:
- Operational – Are you able to complete your work normally? Can you deliver products and services? File legal briefs?
- Monetary – Can your organization handle unexpected costs? Disruptions to revenue streams? Increased insurance premiums?
- Symbolic – What does an attack do to your brand? What if your name is tarnished in the market? What if you’re forced to deal with employee and client churn?
It’s clear ransomware isn’t simply a threat to your organization’s bank accounts. It’s a full, three-dimensional threat, the implications of which will affect your business top to bottom if you’re not truly prepared. Too many organizations view IT security as a cost center. Ransomware is all but guaranteed to affect your business at some point, and the potential damages can be measured in millions of dollars. When you weigh that risk against a $10,000 annual investment in security measures and organizational training that greatly mitigates your exposure, the monetary benefit becomes obvious.
What Do You Need to Be Prepared?
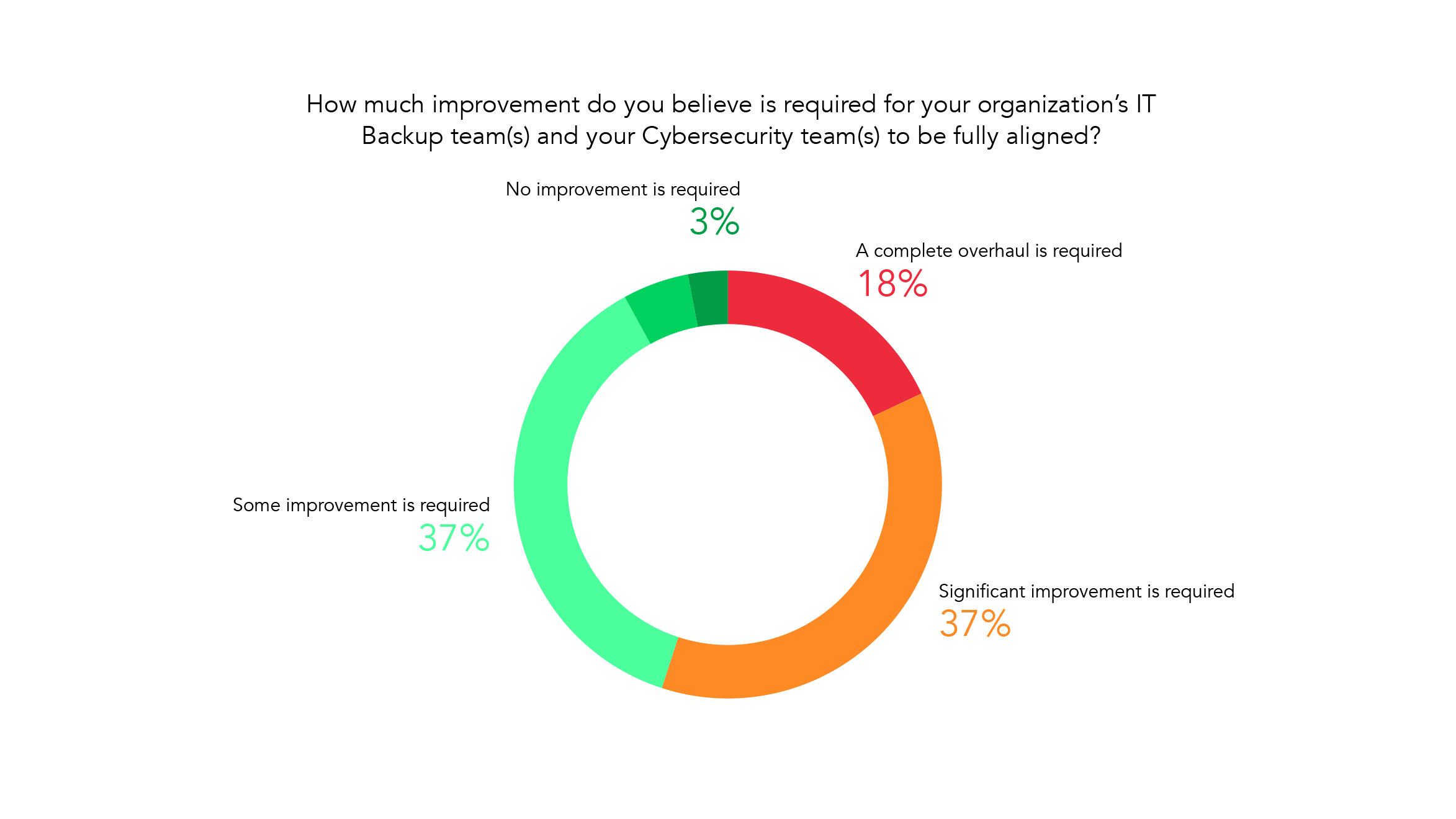
Unfortunately, most organizations recognize that significant changes and investments need to be made into their IT teams. Usually, this is because the right stakeholders aren’t properly looped in on the annual IT planning. IT maturity starts with ensuring your security and backup teams are aligned with executive leadership, so those important stakeholders understand how at-risk the business is.
Atomic Data’s experts ascertain that businesses often get lost in focusing on what’s bright and shiny. These days, for example, every organization is looking to see what an investment in artificial intelligence (IT) can do for them. Too often, this focus on the new and exciting comes at a cost to the basic fundamentals. As we’ve seen, the threat landscape is ever-changing, which means your defense posture must be fluid as well.

“An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure”
Tim Grosshuesch, vCIO
There Is No Silver Bullet for Ransomware Resilience
- The human element is often the weakest link
- Always take a multi-faceted approach
- Defense in Depth – like a castle with a moat, walls, sentries, archers, and interior walls
- Prevention and mitigation requires a deep dive into your business – question what you are, and are not doing using a framework like CIS
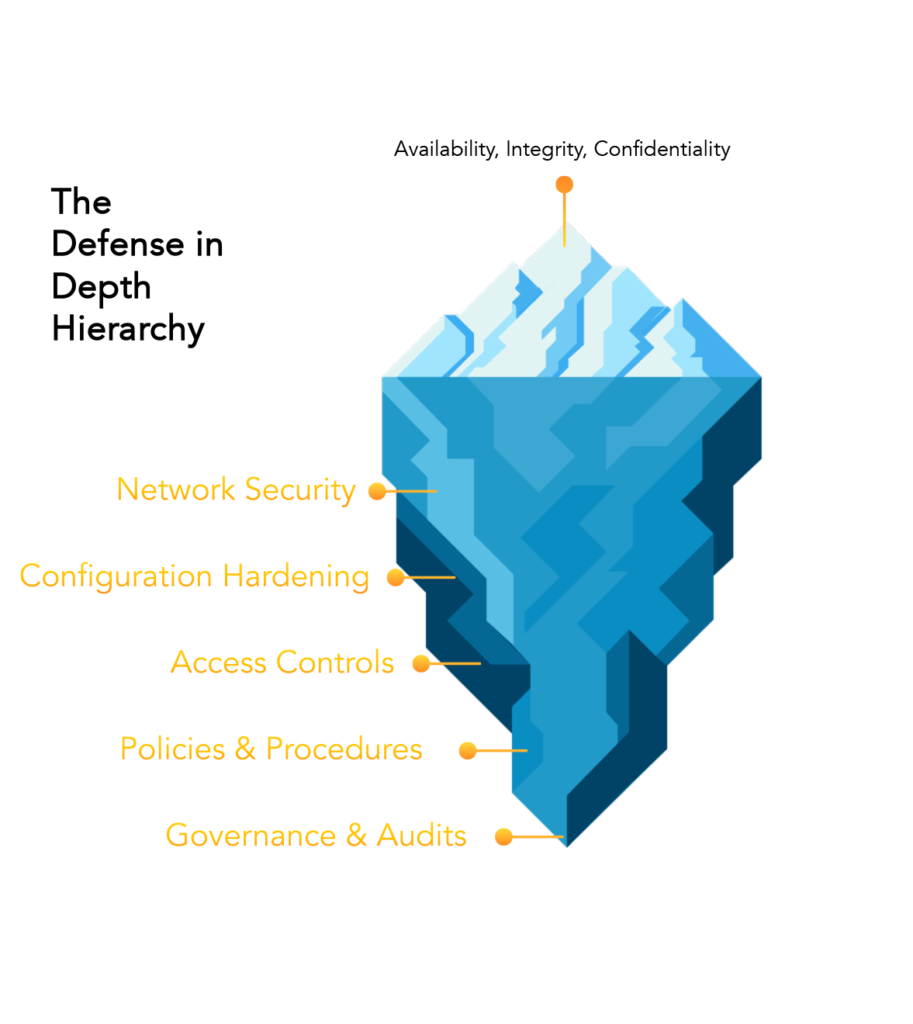
Adopt a Framework: CIS Security Controls
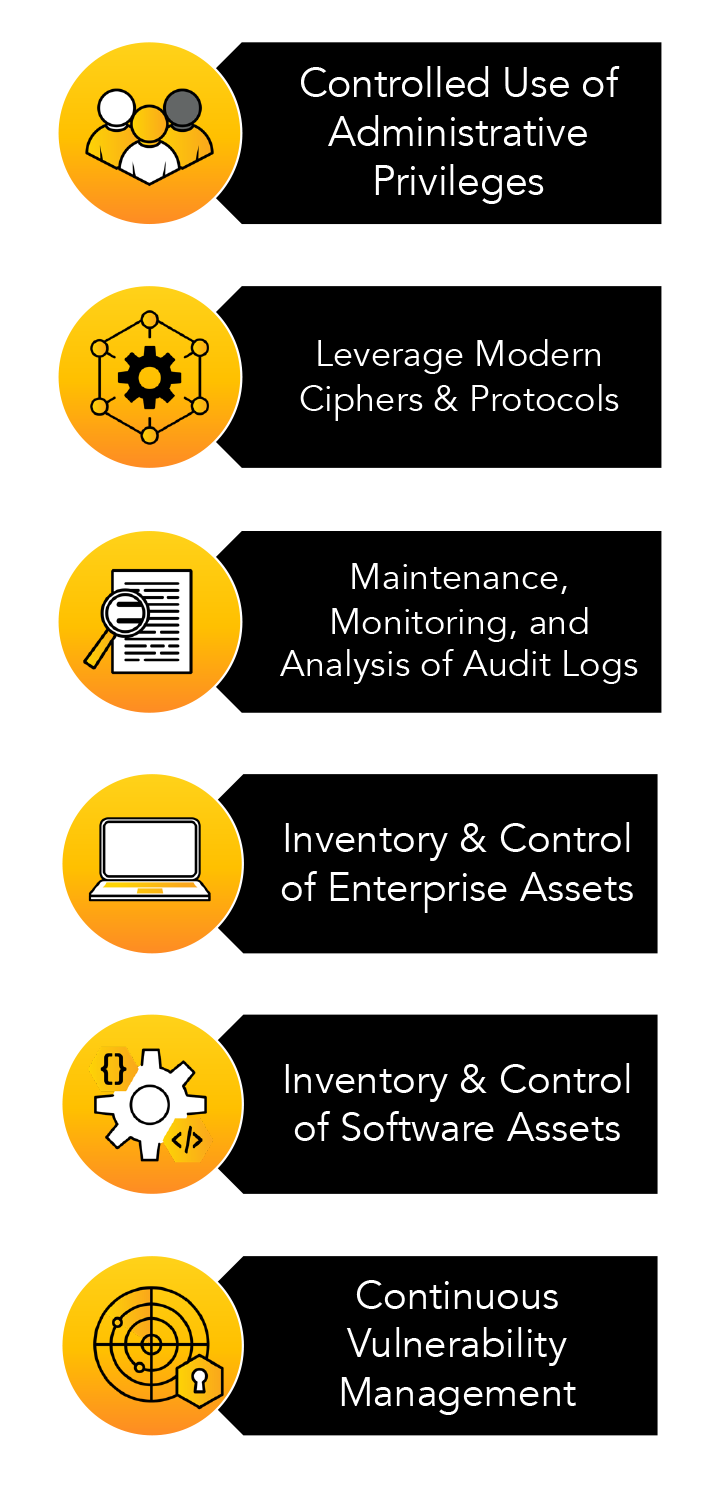
While there are many different benchmarks that are public, several are industry specific. Atomic Data bases its best practices around the 18 CIS Security Controls. This is because they’re public, easy to use, and relevant to most every organization. The list looks like a lot, because they encompass everything that could be within your environment: Atomic Data’s experts recommend that businesses start with what brings in the clearest return on investment.
Thankfully, these are often not the most expensive pieces of software. It’s things such as:
- Have you disabled old protocols?
- Do you know what’s on your network?
- Do you have an inventory of all assets?
- Do you turn down accounts when people leave your organization?
- Are account privileges in place, and updated?
- Are you doing routine maintenance?
- Do you monitor your environment around the clock?
A Perfect Storm of Complexity and Threats

Data Explosion
150+ ZB created in 2024 and doubling every year

Infrastructure Complexity
92% of enterprises have a multi-cloud strategy

Vendor Lock-in
Every 3 years, expect to experience an IT hardware refresh

Surge in Ransomware Complexity
27% of organizations paid the ransom, and never got their data back
Now, what do you do when the worst happens, and you’re impacted by a ransomware strike? To start, it’s important to recognize that data is the lifeblood of every business, and presents increasingly complex challenges for organizations like yours to manage. As data explodes year on year, and sprawls across multiple clouds, countless endpoints and geographic locations, Veeam is tracking two emerging threats to data resilience.
The first is vendor lock-in. To keep data resilient, you need the ability to move your data easily to new applications or platforms, especially as the industry tracks aggressive vendor price increases, sending budgets spiraling.
The second is the increasing volume and sophistication of ransomware – a costly problem, especially when you consider that 27% of organizations who paid a ransom still couldn’t recover their data.
It’s important to remember that resilience, like anything else, is a journey. Continuously improving is the key.
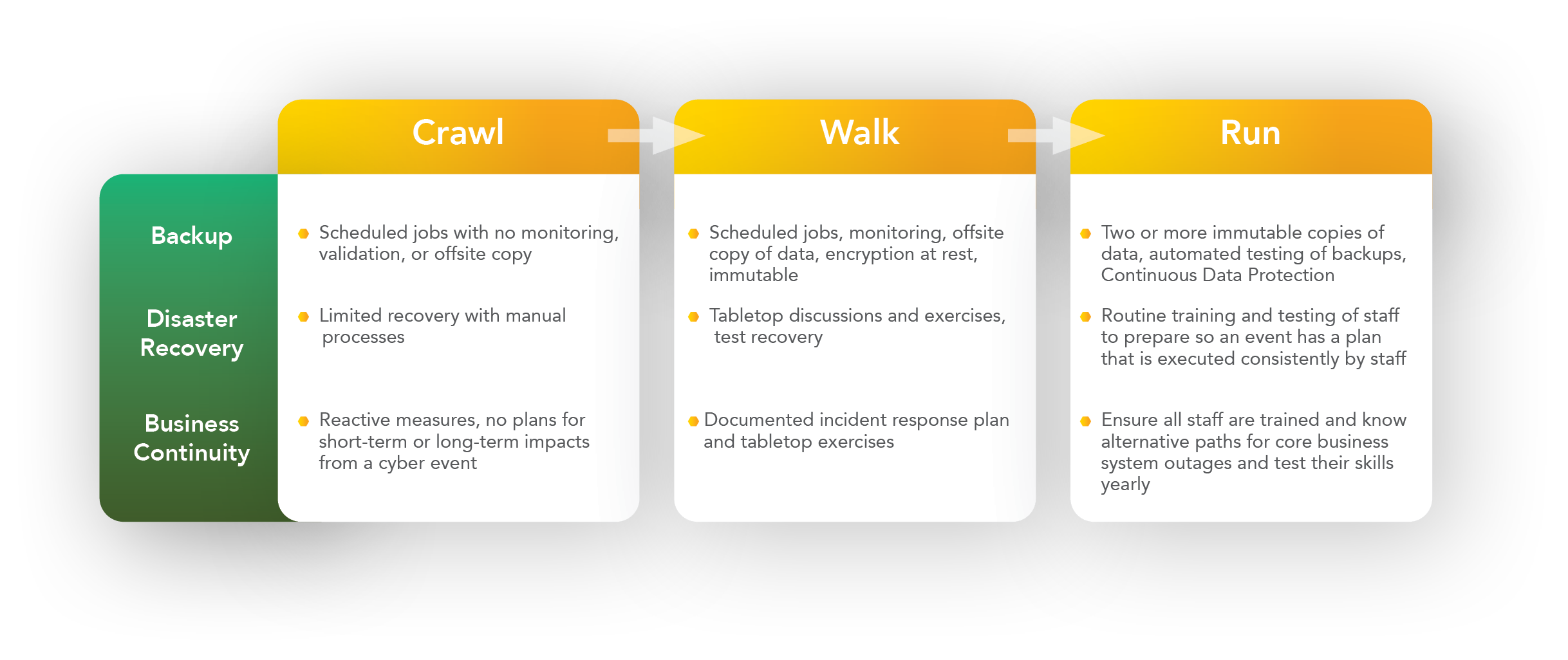
Total Data Protection for Ransomware Resilience
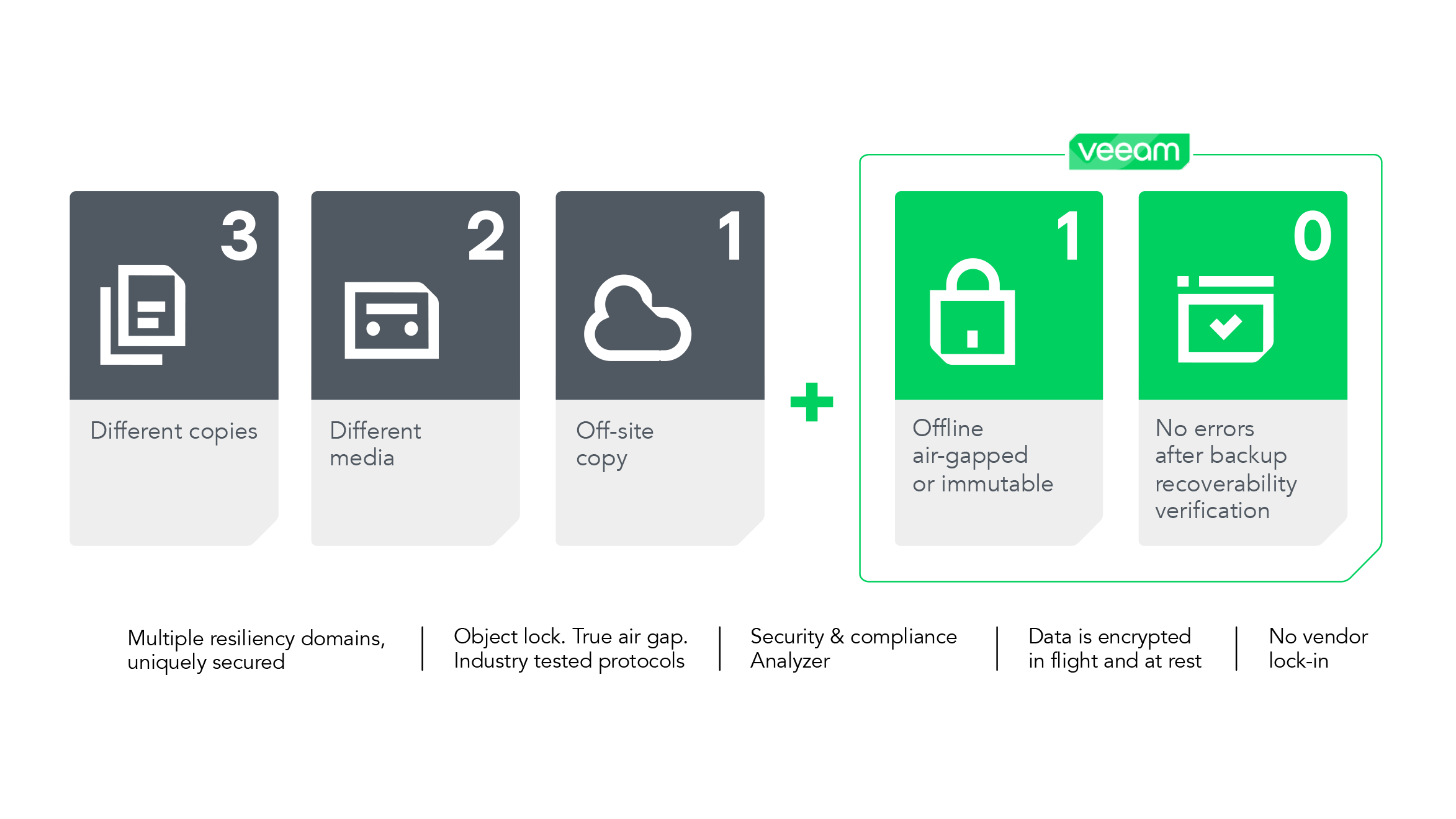
When it comes to data protection, the industry-standard approach of the 3-2-1 rule is something many organizations practice by default. While this was the gold standard for many years, it simply is not enough in the age of ransomware. Organizations need to go a step further and ensure they have an immutable copy of their data and have done comprehensive testing to ensure there are no errors in the data. Put another way, it is now the 3-2-1-1-0 rule, or the “zip code of availability.”
Three copies of your data (production, backup repository, tape)
Two different types of media (disk and tape)
One offsite copy – this can be either your backup repository or tape library
One of which is air-gapped or immutable – Tape can be either, or both when using WORM media
Zero errors – Tools such as Veeam’s SureBackup can be leveraged for automatic and customized testing, ensuring that each backup job is fully recoverable
This gives you powerful immutability options which allows you to protect data from your performance tier to your archives, both on premises and in the cloud.
VDP Respond – Recover Faster from Ransomware
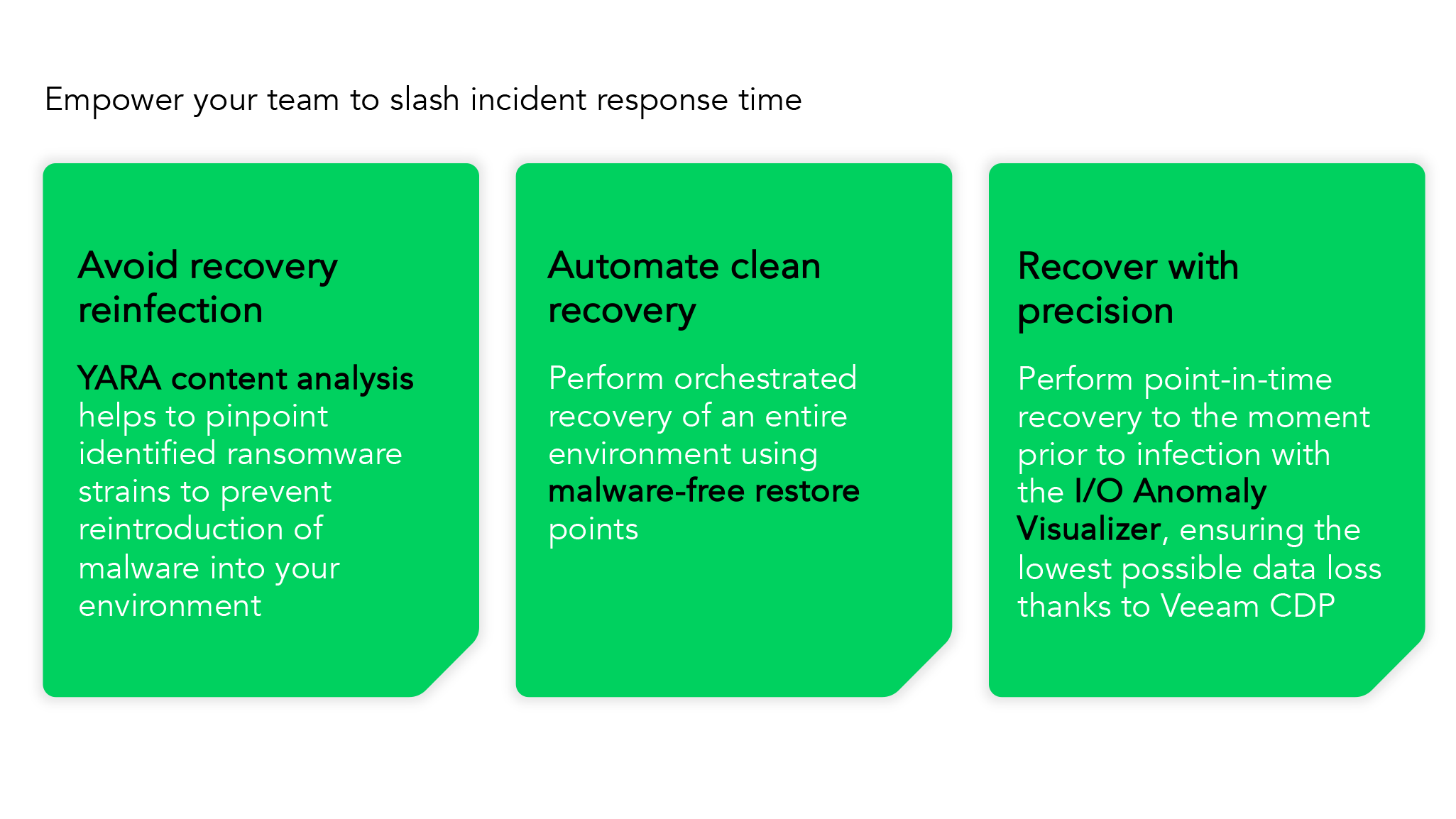
Reinfection is going to be a top concern of your IT and cybersecurity teams after an attack. With the Veeam Data Platform, your teams can leverage YARA content analysis to recover clean the first time.
What is YARA? It stands for “yet another recursive acronym”, but it’s simply an open-source mechanism to help malware researchers identify and classify malware. Within the Veeam Data Platform, the YARA content analysis uncovers and confirms identified ransomware strains in your backups with pinpoint precision to avoid reinfection.
Additionally, Veeam’s new I/O Anomaly Visualizer makes your team aware of potentially anomalous disk activity during backup and, using continuous data protection, you can now roll back to a moment before infection with split-second precision.
Every second counts after an attack. Ensure your teams are using tested, orchestrated recovery from an industry leader and a trusted partner.
Data Observability at your Fingertips with Veeam ONE
Veeam ONE is a premier analytics and monitoring tool. It hits the ground running, analyzing information from your environment and developing an understanding of what is normal, and what’s suspicious. This allows you to highlight threats, identify risks, and get deep insights into your environment’s security via a security score, found in the Veeam Threat Center Dashboard. This score factors in the security protocols in your backup environment, ascertaining whether those backups are meeting your organizational objectives or not. With detailed alarms and reports, this can be a powerful tool for getting a one-glance look at your weak points.

Closing Thoughts and Top Takeaways for Ransomware Resilience
Ultimately, engaging in best practices will go a long way toward ensuring your organization’s ransomware resilience. Good hygiene in your backups is going to give you invaluable recovery options when you’re ultimately hit by an attack. Finally, around-the-clock monitoring is going to be key in ensuring you can swiftly identify and defend against threat actors who have found their way into your environment.
The November 12 webinar was conducted by Tim Grosshuesch, vCIO from Atomic Data, and Kirsten Stoner, Technologist from Veeam.

Related Links
